Introduction
About Washim Zilla Parishad

Panchayati Raj is an innovative experiment in the creation of modern India. The Balwantrai Mehta Committee recommended a three-tier Panchayati Raj system to involve rural people in rural development. Based on this recommendation, the Maharashtra Government enacted the Maharashtra Zilla Parishads and Panchayat Samitis Act, 1961, and established a
three-tier Panchayati Raj system consisting of Zilla Parishad at the district level, Panchayat Samiti at the block level, and Gram Panchayat at the village level. Washim Zilla Parishad was established on July 1, 1998. Presently, 6 Panchayat Samitis and 491 Gram Panchayats are actively working for the development of rural areas. Through the 73rd Constitutional Amendment, women have been given a significant role in governance, and Gram Panchayats have been empowered through Gram Sabhas. Washim Zilla Parishad has consistently been at the forefront of implementing government schemes, campaigns, and initiatives.
Key Facts :
- Establishment of Washim ZP: July 1, 1998
- Total Talukas/Panchayat Samitis: 6
- Total Villages: 789
- Total Gram Panchayats: 491
- Independent Gram Panchayats: 327
- Group Gram Panchayats: 164
- Primary Health Centers: 25
- Sub Centers: 153
- Primary Schools: 1,027
- Secondary Schools: 337
- Veterinary Hospitals: 58
- Total Livestock: 446,288
- Integrated Child Development Projects: 6
- Anganwadis: 1,076
- Kolhapuri Dams (Irrigation Capacity in Hectares): 3,340
- Percolation Tanks (Irrigation Capacity in Hectares): 5,574 ha
- Irrigation Ponds (Irrigation Capacity in Hectares): 4,383 ha
- Storage Reservoirs: 672 ha
- Average Rainfall: 750 to 1000 mm
- Climate: Hot, Arid
Census 2011 Data:
- Total Population: 1,197,160
- Urban: 211,413
- Rural: 985,747
- scheduled Castes: 229,462
- Scheduled Tribes: 80,471
- Literacy Rate: 74.03%
- Sex Ratio: 926 females per 1,000 males
- Population Density: 230 per sq km
About Washim District
The ancient name of Washim was Vatsagulma or Vatsulgram. It was also known as Bachhom or Basam. The Satavahanas ruled here around 300 BCE. In ancient Vidarbha, administrative capitals were established at two places: one in Washim and the other at Nandivardhan (now Nagardhan) in the Ramtek taluka of Nagpur. Washim was once the capital of the Vakataka dynasty, which made significant contributions to literature. During their reign, the region of Vatsagulma had numerous pilgrimage sites, including the well-known Balaji temple and the Padmateerth shrine.
After the Vakatakas, the Chalukyas ruled the region, shifting their capital elsewhere, diminishing Washim’s importance. During the Yadava rule, the city’s significance grew once again. Later, when the British took over the Berar region, they established Washim as the district headquarters. However, during the reorganization of Maharashtra’s districts in 1905, Washim was merged with the neighboring Akola district. On July 26, 1998, it was officially declared a separate district.
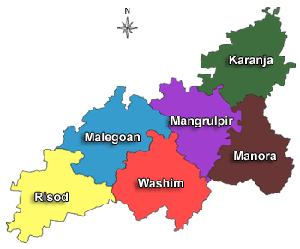
Geography
Washim is located in the eastern part of Vidarbha. It is bordered by Akola to the north, Amravati to the northeast, Hingoli to the south, Buldhana to the west, and Yavatmal to the east. The primary river in the district is the Penganga, flowing through the Risod tehsil and forming the boundary between Washim and Hingoli. The Kas river, a major tributary of the Penganga, passes through Shelgaon Rajgure village. The Arunavati river, originating in Washim taluka, flows into Yavatmal district. Similarly, the Katepurna river originates from the hilly regions of Washim and flows northward into Akola district.



